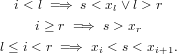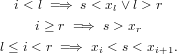22.4 Array
599⟨dom: Array 599⟩≡ (569a)
Array(S: Type): with {
⟨exports: Array 600⟩
} == IndexedOneDimensionalArray(S, 0$Integer) add {
Rep == IndexedOneDimensionalArray(S, 0$Integer);
import from Rep;
⟨implementation: Array 601a⟩
}
Defines:
Array, used in chunks 105, 108, 110, 111a, 137, 139–41, 147, 148, 157, 185b, 186, 188b,
189, 228, 272, 347, 375, 537, 557–59, 562b, 608, 609, 626, 628, 648–50, 652, 654, 655,
657, 658, 660, 688a, 700, 727, 729, 731, and 732.
Uses Integer 66.
Exports of Array
-
-
if S has PrimitiveType then PrimitiveType;
-
-
if S has OutputType then OutputType;
-
-
if S has SetCategory then SetCategory;
-
-
#: % -> I
-
-
bracket: Tuple S -> %
-
-
new: (I, S) -> %
-
-
new: I -> %
-
-
apply: (%, I) -> S
-
-
set!: (%, I, S) -> S
-
-
generator: % -> Generator S
-
-
data: % -> ACPrimitiveArray S
-
-
if S has TotallyOrderedType then {
-
-
binarySearch: (S, %) -> (Boolean, I)
-
-
}
600⟨exports: Array 600⟩≡ (599) 601b ⊳
if S has PrimitiveType then PrimitiveType;
Cannot use the Axiom code since that (unnecessarily) requires S to be of type
SetCategory.
601a⟨implementation: Array 601a⟩≡ (599) 601c ⊳
if S has PrimitiveType then {
(x: %) = (y: %): Boolean == {
import from I, S;
(n := #x) ~= #y => false;
last: Integer := prev(n)::Integer;
for z in 0..last repeat {
if rep(x).z ~= rep(y).z then return false;
}
true;
}
}
Uses I 47 and Integer 66.
601c⟨implementation: Array 601a⟩+
≡ (599) ⊲601a 602b ⊳
if S has OutputType then {
(tw: TextWriter) << (x: %): TextWriter == {
import from S, ACString;
tw := tw << "[";
firstElement?: Boolean := true;
for s in x repeat {
if not firstElement? then tw := tw << ", ";
tw := tw << s;
firstElement? := false;
}
tw << "]";
}
}
Uses ACString 579 and OutputType 570.
We must convert from NonNegativeInteger to ACMachineInteger.
602d⟨implementation: Array 601a⟩+
≡ (599) ⊲602b 603a ⊳
bracket(s: Tuple S): % == {
import from List S, SingleInteger;
per construct [element(s, i) for i in 1..length s]
}
603a⟨implementation: Array 601a⟩+
≡ (599) ⊲602d 603c ⊳
new(sz: I, s: S): % == {
import from NonNegativeInteger;
per new(sz :: NNI, s);
}
Uses I 47.
In Axiom – contrary to Aldor– new always takes a second argument that holds
the element with which the new array should be initialized. Thus we have to
improvise a little here.
ToDo ⊲ 85 ⊳ rhx ⊲ 67 ⊳ 21-Dec-2006: Potentially dangerous to rely on the right
size of
0$Integer!
Unfortunately, we need a dummy element from the parameter domain S. Hopefully,
that will have the right size.
603c⟨implementation: Array 601a⟩+
≡ (599) ⊲603a 604b ⊳
new(sz: I): % == {
dummyElement: S == (0$Integer) pretend S;
new(sz, dummyElement);
}
Uses I 47 and Integer 66.
606b⟨exports: Array binarySearch 606b⟩≡ (606a)
binarySearch: (S, %) -> (Boolean, I);
Uses I 47.
606d⟨implementation: Array binarySearch 606d⟩≡ (606c) 607 ⊳
binarySearch(s: S, x: %): (Boolean, I) == {
import from I;
binarySearch(s, x, 0, prev #x);
}
Uses I 47.
The following function returns (b,i) with b = true and l ≤ i ≤ r if s = xi.
Otherwise b = false and one of the following is true.
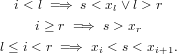 |
(185)
(186)
(187)
|
This specification is in accordance with the one from binarySearch
of the package BinarySearch from Algebra.
607⟨implementation: Array binarySearch 606d⟩+
≡ (606c) ⊲606d
binarySearch(s: S, x: %, l: I, r: I): (Boolean, I) == {
assert(l>=0);
assert(r<#x);
i: I := shift(l+r, -1); -- (l+r)/2
i < l => (false, i); -- l > r
xi := x.i;
s = xi => (true, i);
s < xi => binarySearch(s, x, l, prev i);
binarySearch(s, x, next i, r);
}
Uses I 47.
The above function passes the following tests.
608a⟨test binarySearch 608a⟩≡ 608b ⊳
checkSearch(a: Array I, i: I, b: Boolean, idx: I): () == {
import from I, SmallIntegerTools;
(found?, i) := binarySearch(i, a);
assertEquals(Boolean, b, found?);
assertEquals(I, idx, i);
}
testbSearch1(): () == {
import from I, SmallIntegerTools;
a: Array I := [0];
checkSearch(a, -1, false, -1);
checkSearch(a, 0, true, 0);
checkSearch(a, 1, false, 0);
}
Uses Array 599, I 47, and SmallIntegerTools 555.
testbSearch2(): () == import from I, SmallIntegerTools; a: Array I := [0, 2];
checkSearch(a, -1, false, -1); checkSearch(a, 0, true, 0); checkSearch(a, 1, false, 0);
checkSearch(a, 2, true, 1); checkSearch(a, 3, false, 1);
608b⟨test binarySearch 608a⟩+
≡ ⊲608a 609 ⊳
testbSearch3(): () == {
import from I, SmallIntegerTools;
a: Array I := [0, 2, 4];
checkSearch(a, -1, false, -1);
checkSearch(a, 0, true, 0);
checkSearch(a, 1, false, 0);
checkSearch(a, 2, true, 1);
checkSearch(a, 3, false, 1);
checkSearch(a, 4, true, 2);
checkSearch(a, 5, false, 2);
}
Uses Array 599, I 47, and SmallIntegerTools 555.
609⟨test binarySearch 608a⟩+
≡ ⊲608b
testbSearch4(): () == {
import from I, SmallIntegerTools;
a: Array I := [0, 2, 4, 6];
checkSearch(a, -1, false, -1);
checkSearch(a, 0, true, 0);
checkSearch(a, 1, false, 0);
checkSearch(a, 2, true, 1);
checkSearch(a, 3, false, 1);
checkSearch(a, 4, true, 2);
checkSearch(a, 5, false, 2);
checkSearch(a, 6, true, 3);
checkSearch(a, 7, false, 3);
}
Uses Array 599, I 47, and SmallIntegerTools 555.