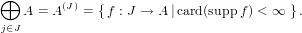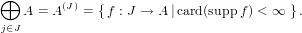17.2 SparseAdditiveArray
The domain IndexedFreeAdditiveCombinationType basically is an
implementation of a polynomial domain that lacks multiplication. In fact, we can
consider the type A as being an additive semigroup which is not necessarily
commutative.
Type Constructor
SparseAdditiveArray
Description
Additive monoid of functions with finite support.
The domain constructor implements
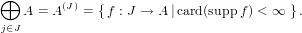 |
(177)
|
Parameters
-
A:
-
An additive monoid.
-
J:
-
A totally ordered index set.
489⟨dom: SparseAdditiveArray 489⟩≡ (462)
SparseAdditiveArray(
A: with {
zero?: % -> Boolean;
+: (%, %) -> %;
},
J: TotallyOrderedType
): IndexedFreeAdditiveCombinationType(A, J) == add {
macro Pair == Cross(A, J);
Rep == List Pair;
import from Pair, Rep;
⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray: auxiliary 491a⟩
⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩
}
Defines:
SparseAdditiveArray, used in chunks 501, 506, 733, 736a, 739, and 740.
Uses IndexedFreeAdditiveCombinationType 465 and TotallyOrderedType 571.
490a⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩≡ (489) 490b ⊳
0: % == per empty;
490b⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲490a 490c ⊳
zero?(x: %): Boolean == empty? rep x;
490c⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲490b 490d ⊳
bracket(a: A, j: J): % == {
zero? a => 0;
aj: Cross(A, J) := (a, j);
per [aj];
}
490d⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲490c 491b ⊳
(x: %) + (y: %): % == {
import from A, J, I;
zero? x => y;
zero? y => x;
(xa, xj) := xm := leadingMonomial x;
(ya, yj) := ym := leadingMonomial y;
c := compare(xj, yj);
c > 0 => TOPADD(xm, reductum x + y);
c < 0 => TOPADD(ym, x + reductum y);
a: A := xa + ya;
z: % := reductum x + reductum y;
if not zero? a then z := topAdd(a, xj, z);
z;
}
Uses I 47.
The auxiliary function is a way to add a monomial when it is already known that
j is bigger than any index in x.
491a⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray: auxiliary 491a⟩≡ (489)
macro TOPADD(m, x) == per cons(m, rep x);
local topAdd(a: A, j: J, x: %): % == {
import from I;
assert(zero? x or j > maxSupport x);
assert(not zero? a);
aj: Cross(A, J) := (a, j);
TOPADD(aj, x);
}
Uses I 47.
491b⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲490d 491c ⊳
leadingMonomial(x: %): Cross(A, J) == {
assert(not zero? x);
first rep x;
}
491c⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲491b 491d ⊳
reductum(x: %): % == {
assert(not zero? x);
per rest rep x;
}
492b⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲492a 492c ⊳
map(f: A -> A)(x: %): % == {
per [((a,j):=m; mm:=(f(a),j)) for m in x];
}
492c⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲492b 492d ⊳
map(f: Cross(A,J) -> Cross(A,J))(x: %): % == per map(f) rep x;
492d⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray 490a⟩+
≡ (489) ⊲492c
if A has with {-: (%, %) -> %; -: % -> %} then {
⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray: minus 493⟩
}
493⟨implementation: SparseAdditiveArray: minus 493⟩≡ (492d)
(x: %) - (y: %): % == {
import from A, J, I;
zero? x => -y;
zero? y => x;
(xa, xj) := xm := leadingMonomial x;
(ya, yj) := ym := leadingMonomial y;
c := compare(xj, yj);
c > 0 => TOPADD(xm, reductum x - y);
c < 0 => {ym := (-ya, yj); TOPADD(ym, x - reductum y);}
a: A := xa - ya;
z: % := reductum x - reductum y;
if not zero? a then z := topAdd(a, xj, z);
z;
}
Uses I 47.